The objective of this research is that The Artificial Brain has to provide the robot with abilities to perceive an environment, to interact with humans, to make intelligent decision and to learn new skills.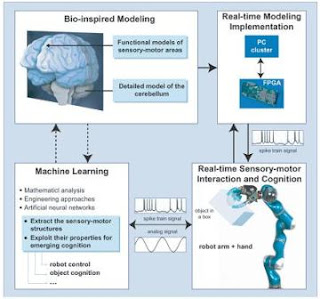
An international team of European researchers has implanted an artificial cerebellum — the portion of the brain that controls motor functions — inside a robotic system. This EU-funded project is dubbed SENSOPAC, an acronym for ‘SENSOrimotor structuring of perception and action for emerging cognition.’
One of the goals of this project is to design robots able to interact with humans in a natural way. This project, which should be completed at the end of 2009, also wants to produce robots which would act as home-helpers for disabled people, such as persons affected by neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease.
The European SENSOPAC project started on January 1, 2006 and will take 4 years to be completed. The 12 organizations participating to the project come from 9 different countries and have provided physicists, neuroscientists and electronic engineers.
The microchips which incorporate a full neuronal system have been designed at the University of Granada, Spain. “Implanting the man-made cerebellum in a robot will allow it to manipulate and interact with other objects with far greater effectiveness than previously managed.
‘Although robots are increasingly more important to our society and have more advanced technology, they cannot yet do certain tasks like those carried out by mammals,’ says Professor Eduardo Ros Vidal, who is coordinating the work at the University of Granada. ‘We have been talking about humanoids for years but we do not yet see them on the street or use the unlimited possibilities they offer us,’ the Professor added.”
Also
A team of South Korean scientists has made a breakthrough in developing an artificial brain system, which enables a robot to make a decision in tune with different situations.
The team, headed by Prof. Kim Jong-hwan at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, said Thursday that they are trying to incorporate the system to physical robots.
The brain system is a software robot, called sobot, which imitates the thinking mechanism architecture of human brains from sensing to decision-making and behaviors.
Kim said the new-fangled software robot is the world's first one that can make a decision based on contexts, or check surroundings before opting on how to behave.
''Let me take an example. When an owner returns home, a robot is charging its battery. Then, it is supposed to stop consuming electricity and greet the human,'' Kim said.
``When the machine charged itself enough, it will know so. But if its battery runs low, it will select to remain being plugged in. In other words, it thinks close to a human,'' he said.
Emulating the human brain, the software robot is composed of six modules for as many functions perception, context awareness, internal status, memory, behavior and actuator.
``We will continue to put forth efforts to enhance the capacity of software robots in analyzing the environment and reaching conclusions before taking actions,'' Kim said. ``Such attempts will eventually lead to the development of human-like robots.''
KT, the country's predominant telecom operator, already recognized the exponential potential of the sophisticated system.
Beginning next month, Kim's team will carry out a joint research program together with KT regarding the smart software architecture.
Kim is well known globally for founding and leading the Federation of International Robot Soccer, where robotic drones duke it out on the pitch.
He also gained prominence in late 2004 by unveiling a software robot, which is programmed with 14 artificial chromosomes that control a total of 77 behaviors.
According to Kim, the software robot, which he claims evolves through crossover and mutation, can offer personality to robot hardware.
Monday, March 24, 2008
Artificial Brain
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


No comments:
Post a Comment