A Microcontroller (also MCU or µC) is a computer-on-a-chip. It is a type of microprocessor emphasizing high integration, low power consumption, self-sufficiency and cost-effectiveness, in contrast to a general-purpose microprocessor (the kind used in a PC).
Microcontrollers are frequently used in automatically controlled products and devices, such as automobile engine control systems, remote controls, office machines, appliances, robotics power tools, and toys. By reducing the size, cost, and power consumption compared to a design using a separate microprocessor, memory, and input/output devices, microcontrollers make it economical to electronically control many more processes.
Embedded design:
The majority of computer systems in use today are embedded in other machinery, such as telephones, clocks, appliances, and vehicles. An embedded system may have minimal requirements for memory and program length. Input and output devices may be discrete switches, relays, or solenoids. An embedded controller may lack any human-readable interface devices at all. For example, embedded systems usually don't have keyboards, screens, disks, printers, or other recognizable I/O devices of a personal computer. Microcontrollers may control electric motors, relays or voltages, and may read switches, variable resistors or other electronic devices.
Programming Environments:
Microcontrollers were originally programmed only in assembly language, but various high-level programming languages are now also in common use to target microcontrollers. These languages are either designed specially for the purpose, or versions of general purpose languages such as the C programming language. Compilers for general purpose languages will typically have some restrictions as well as enhancements to better support the unique characteristics of microcontrollers.
Interpreter firmware is also available for some microcontrollers. The Intel 8052 and Zilog Z8 were available with BASIC very early on, and BASIC is more recently used in the BASIC Stamp MCUs.Some microcontrollers have environments to aid developing certain types of applications, e.g. Analog Device's Blackfin processors with the LabVIEW environment and its programming language "C".
Simulators are available for some microcontrollers, such as in Microchip's MPLAB environment. These allow a developer to analyse what the behaviour of the microcontroller and their program should be if they were using the actual part. A simulator will show the internal processor state and also that of the outputs, as well as allowing input signals to be generated. While on the one hand most simulators will be limited from being unable to simulate much other hardware in a system, they can exercise conditions that may otherwise be hard to reproduce at will in the physical implementation, and can be the quickest way to debug and analyse problems.
Recent microcontrollers integrated with on-chip debug circuitry accessed by In-circuit emulator via JTAG enables a programmer to debug the software of an embedded system with a debugger.
Use of MICROCONTROLLERS in ROBOTIC’S depends on the requirement.
Click On This Link To Get A List Of Different MICROCONTROLLER’S Manufactured By Differnt Companies
Few of the Companies which manufacture MICROCONTROLLER’S are stated below:
1) ATMEL Corporation: It is a manufacturer of semiconductors, founded in 1984. Its focus is on system-level solutions built around flash microcontrollers. Its products include microcontrollers (including 8051 derivatives and AT91SAM and AT91CAP ARM-based micros), and its own ATMEL AVR and AVR32 architectures, radio frequency (RF) devices, EEPROM and Flash memory devices (including DataFlash-based memory), and a number of application-specific products. ATMEL supplies its devices as standard products, ASICs, or ASSP's depending on the requirements of its customers. In some cases it is able to offer system on chip solutions.
ATMEL serves a range of application segments including consumer, communications, computer networking, industrial, medical, automotive, aerospace and military. It is an industry leader in secure systems, notably for the smart card market.
Few of ATMEL Microcontroller’s
• AT89 series (Intel 8051 architecture)
• AT90, ATtiny, ATmega series (AVR architecture) (Atmel Norway design)
• AT91SAM (ARM architecture)
• AVR32 (32-bit AVR architecture)
• MARC4
2)Cypress MicroSystems :
(CMS) (not to be mistaken with the cypress tree) markets high-performance, field Programmable System-on-a-Chip (PSoC) integrated M8 micro-based solutions. CMS is based in Lynnwood, near Seattle, Washington and was established as a subsidiary of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation in the fourth quarter of 1999. Who's one of the best engineer is Bert Sullam. Now cypresses micro chips has grown from a small simple chip too one of the best and highest quality micro chips now you can find it any where.
Cypress MicroSystems was purchased by Cypress Semiconductor in the 4th quarter of 2005 consistent with the original business plan of the start up.
More Updates Soon Please Bear For Mean Time And If Any Specific Request Please A Comment.
Friday, March 28, 2008
Microcontrollers
Monday, March 24, 2008
Artificial Brain
The objective of this research is that The Artificial Brain has to provide the robot with abilities to perceive an environment, to interact with humans, to make intelligent decision and to learn new skills.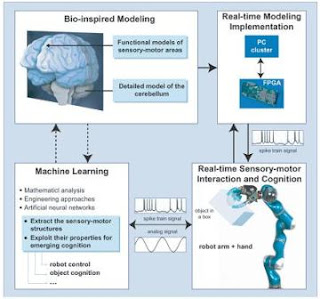
An international team of European researchers has implanted an artificial cerebellum — the portion of the brain that controls motor functions — inside a robotic system. This EU-funded project is dubbed SENSOPAC, an acronym for ‘SENSOrimotor structuring of perception and action for emerging cognition.’
One of the goals of this project is to design robots able to interact with humans in a natural way. This project, which should be completed at the end of 2009, also wants to produce robots which would act as home-helpers for disabled people, such as persons affected by neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease.
The European SENSOPAC project started on January 1, 2006 and will take 4 years to be completed. The 12 organizations participating to the project come from 9 different countries and have provided physicists, neuroscientists and electronic engineers.
The microchips which incorporate a full neuronal system have been designed at the University of Granada, Spain. “Implanting the man-made cerebellum in a robot will allow it to manipulate and interact with other objects with far greater effectiveness than previously managed.
‘Although robots are increasingly more important to our society and have more advanced technology, they cannot yet do certain tasks like those carried out by mammals,’ says Professor Eduardo Ros Vidal, who is coordinating the work at the University of Granada. ‘We have been talking about humanoids for years but we do not yet see them on the street or use the unlimited possibilities they offer us,’ the Professor added.”
Also
A team of South Korean scientists has made a breakthrough in developing an artificial brain system, which enables a robot to make a decision in tune with different situations.
The team, headed by Prof. Kim Jong-hwan at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, said Thursday that they are trying to incorporate the system to physical robots.
The brain system is a software robot, called sobot, which imitates the thinking mechanism architecture of human brains from sensing to decision-making and behaviors.
Kim said the new-fangled software robot is the world's first one that can make a decision based on contexts, or check surroundings before opting on how to behave.
''Let me take an example. When an owner returns home, a robot is charging its battery. Then, it is supposed to stop consuming electricity and greet the human,'' Kim said.
``When the machine charged itself enough, it will know so. But if its battery runs low, it will select to remain being plugged in. In other words, it thinks close to a human,'' he said.
Emulating the human brain, the software robot is composed of six modules for as many functions perception, context awareness, internal status, memory, behavior and actuator.
``We will continue to put forth efforts to enhance the capacity of software robots in analyzing the environment and reaching conclusions before taking actions,'' Kim said. ``Such attempts will eventually lead to the development of human-like robots.''
KT, the country's predominant telecom operator, already recognized the exponential potential of the sophisticated system.
Beginning next month, Kim's team will carry out a joint research program together with KT regarding the smart software architecture.
Kim is well known globally for founding and leading the Federation of International Robot Soccer, where robotic drones duke it out on the pitch.
He also gained prominence in late 2004 by unveiling a software robot, which is programmed with 14 artificial chromosomes that control a total of 77 behaviors.
According to Kim, the software robot, which he claims evolves through crossover and mutation, can offer personality to robot hardware.

